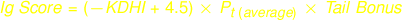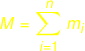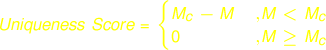|
Process not executed when submitting a FASTA amino acid sequence
|
Consequent
|
|
Extraction of Protein Features
|
Protein Features will not be displayed in the graphical output
|
|
Calculation of Tail Bonus
|
Immunogenicity Score will be calculated without factoring in Tail Bonus
|
|
Calculation of Uniqueness Score
|
Uniqueness Score will not be calculated, the graphical output of Uniqueness Score will be the default brightest yellow, and Uniqueness-optimized rank will be the same as Immunogenicity Score rank
|
|
Calculation of Conservation Score
|
Conservation Score will not be calculated, the graphical output of Conservation Score will be the default black, and Conservation-optimized rank will be the same as Immunogenicity Score rank
|